Measurement of renal function by dried blood spot (DBS) testing
(For the DBS method in animal models, please click here)
We have simplified the measurement of renal function by the plasma clearance of iohexol using the volumetric dried blood spot (DBS) technique, without losing accuracy or precision with respect to the standard method that uses plasma samples. We replaced the plasma samples by micro-samples of capillary blood that are obtained after finger-prick using a painless lancet and collected by a heparinized capillar.
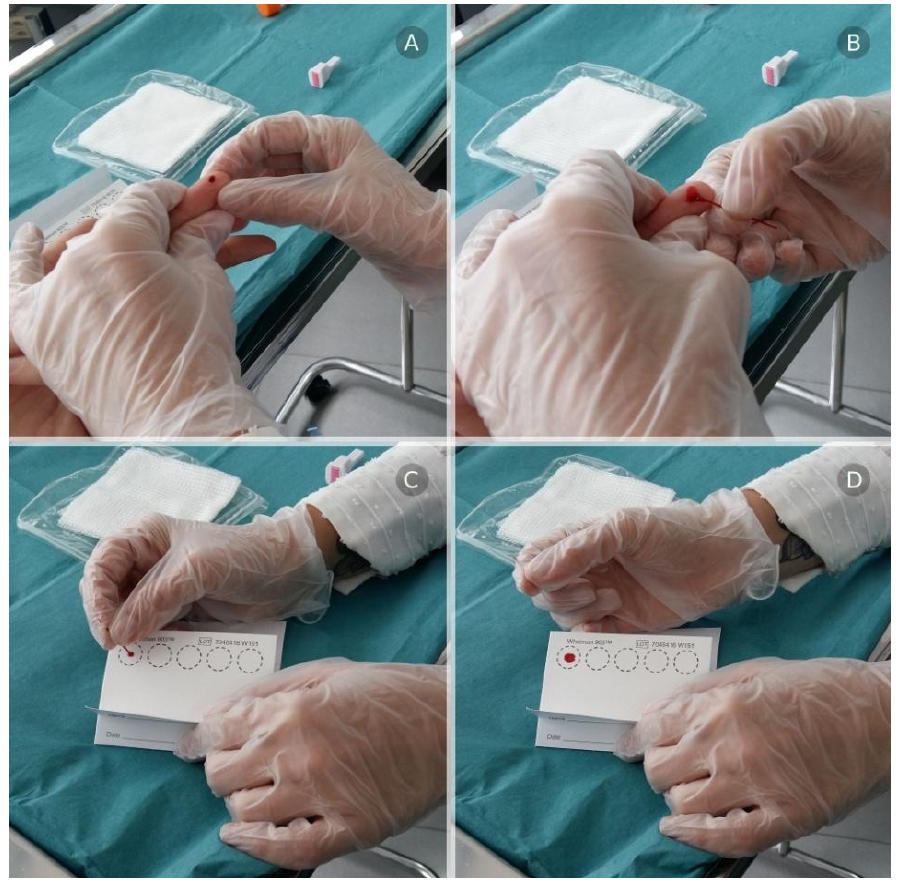
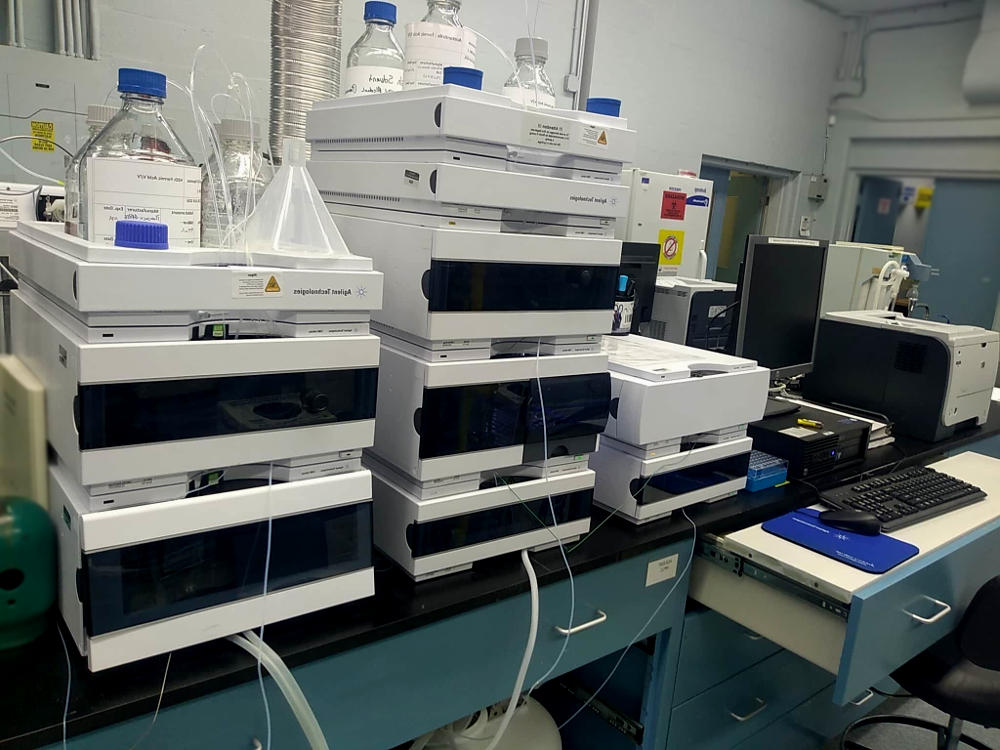
Then, a fixed volume of the micro-sample is placed on a special filter paper (Whatman 903, GE Healthcare) and allowed to dry for a minimum of 8 hours. Finally, iohexol marker is extracted by chemical procedures and analyzed by liquid chromatography (HPLC-UV).

The advantages of this new method are multiple, increasing patient comfort since blood collection is minimal and painless, simplifying all laboratory processes, from the collection of samples to their final analysis, which means a great costs reduction because capillary blood micro-samples can be stored at room temperature and can be sent by regular mail. Finally, there is no need for refrigeration or freezing the sample without the need to be refrigerated throughout the entire process.

We have prepared a web presentation in which we explain in detail the “DBS method”. You can see it at the following address:
Web presentation of the DBS method
Also can be found here an alternative explanation of the DBS method in one downloadable video:
- High quality (resolution 1920×1080, file size 93MB)
- Medium quality (resolution 960×540, file size 22MB)
- Fast download (resolution 480×270, file size 8MB)
Other interesting resources:
